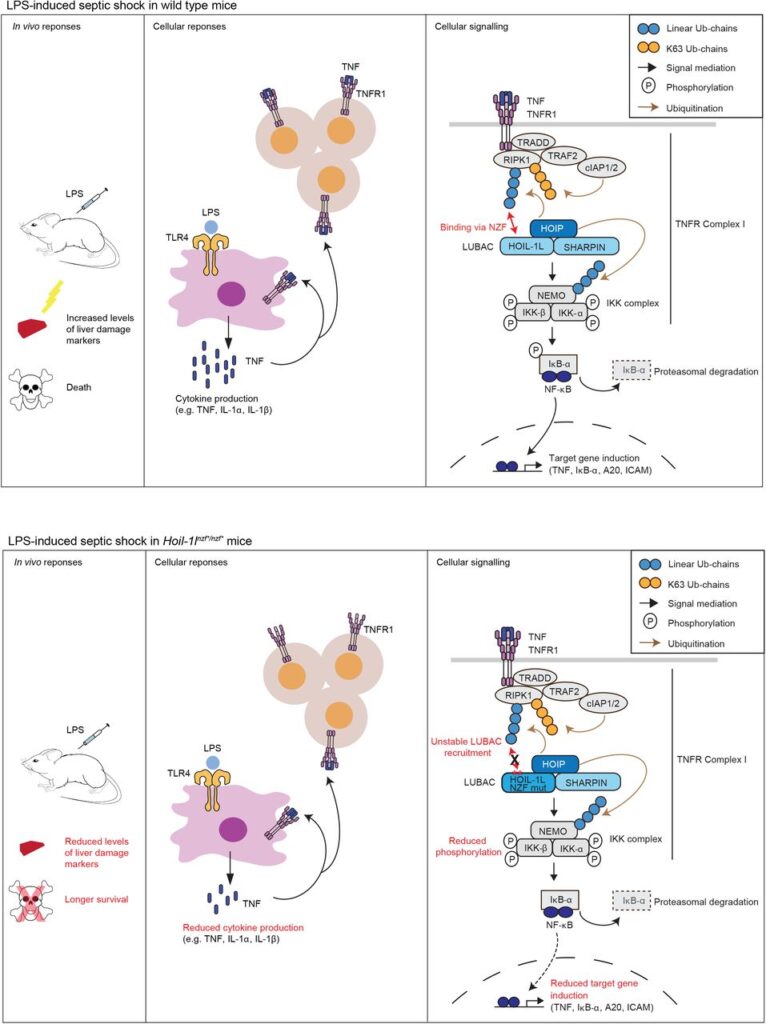
March 22, 2024
Our review article “The emerging roles of non-canonical ubiquitination in proteostasis and beyond” became open online.
Fumiyo as an editorial board member of the JCB organized and wrote together with Stephanie Kaypee (our postdoc), Fumiaki Ohtake and Yoshino Akizuki (the Ohtake Lab).
The Ohtake lab has expertise in the ubiquitin chains called branched chains. We tried to combine our expertise on linear ubiquitination with theirs in this article.
We believe that we covered the most exciting topics from the ubiquitin biology reserach field.
It was a lot of fun writing this with people with slightly different expertise!
 (Wordclouds.com)
(Wordclouds.com)